The tutorial here represents the absolute basics of using the BioDeepTime database. More elaborate tutorials will be made available on Evolv-ED.
Add toc: true to the metadata of the .md file for a table of contents.
The Data
Download
The BioDeepTime database is made available through the ‘chronosphere’ research data API. The R client to access data can be installed from the CRAN servers with:
install.packages("chronosphere") # used to call the data
install.packages("tidyverse") # used for data manipulation and plotting
install.packages("ggrepel") # used for plotting
The most up-to-date version of the denormalized BioDeepTiem database can be accessed with:
# attach package
library(chronosphere)
Chronosphere - Evolving Earth System Variables
Important: never fetch data as a superuser / with admin. privileges!
Note that the package was split for efficient maintenance and development:
- Plate tectonic calculations -> package 'rgplates'
- Arrays of raster and vector spatials -> package 'via'
library(tidyverse)
── Attaching core tidyverse packages ──────────────────────── tidyverse 2.0.0 ──
✔ dplyr 1.1.2 ✔ readr 2.1.4
✔ forcats 1.0.0 ✔ stringr 1.5.0
✔ ggplot2 3.4.2 ✔ tibble 3.2.1
✔ lubridate 1.9.2 ✔ tidyr 1.3.0
✔ purrr 1.0.1
── Conflicts ────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
✖ dplyr::collapse() masks divDyn::collapse()
✖ tidyr::fill() masks divDyn::fill()
✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
✖ dplyr::slice() masks divDyn::slice()
ℹ Use the conflicted package (<http://conflicted.r-lib.org/>) to force all conflicts to become errors
library(ggrepel)
# download data, verbose=FALSE hides the default chatter
bdt <- fetch("biodeeptime", verbose=FALSE)
Note that this table is rather large and might take a bit of time to
load. The accessible data items can be downloaded with
(datasets("biodeeptime")).
Structure
The default representation of the denormalized table is a data.frame,
where every row represents one record or biogeographic observation (the
presence of a taxon in a sample).
str(bdt)
'data.frame': 7437847 obs. of 39 variables:
$ db : chr "Neotoma" "Neotoma" "Neotoma" "Neotoma" ...
$ seriesID : chr "TS_1" "TS_1" "TS_1" "TS_1" ...
$ seriesOriginalName: chr "Konus Exposure, Adycha River" "Konus Exposure, Adycha River" "Konus Exposure, Adycha River" "Konus Exposure, Adycha River" ...
$ seriesOriginalID : chr "11" "11" "11" "11" ...
$ long : num 136 136 136 136 136 ...
$ lat : num 67.8 67.8 67.8 67.8 67.8 ...
$ depthUnit : chr "cmbct" "cmbct" "cmbct" "cmbct" ...
$ ageModel : chr "4" "4" "4" "4" ...
$ reason : chr "Community analysis" "Community analysis" "Community analysis" "Community analysis" ...
$ sampleID : chr "S_1" "S_1" "S_1" "S_1" ...
$ sampleOriginalID : chr "158" "158" "158" "158" ...
$ sampleOriginalName: chr NA NA NA NA ...
$ depth : num 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ age : num 1321 1321 1321 1321 1321 ...
$ ageProc : chr "bchron" "bchron" "bchron" "bchron" ...
$ ageOld : num 2463 2463 2463 2463 2463 ...
$ ageYoung : num 355 355 355 355 355 ...
$ timeOriginalUnit : chr "Radiocarbon years BP" "Radiocarbon years BP" "Radiocarbon years BP" "Radiocarbon years BP" ...
$ timeOriginal : num 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 ...
$ timeOriginalOld : num NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA ...
$ timeOriginalYoung : num NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA ...
$ waterDepth : num NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA ...
$ preservation : chr NA NA NA NA ...
$ samplingEffort : num NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA ...
$ minimumMesh : num NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA ...
$ maximumMesh : num NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA ...
$ environment : chr "Terrestrial or Freshwater" "Terrestrial or Freshwater" "Terrestrial or Freshwater" "Terrestrial or Freshwater" ...
$ samplingEffortType: chr NA NA NA NA ...
$ totalCount : num 809 809 809 809 809 809 809 809 809 809 ...
$ taxonID : int 4 10 3 11 8 1 13 12 5 9 ...
$ analyzedTaxon : chr "Valeriana" "Onagraceae" "Ericaceae" "Cyperaceae" ...
$ species : chr NA NA NA NA ...
$ genus : chr NA NA NA NA ...
$ openNomenclature : chr NA NA NA NA ...
$ analyzedRank : chr NA NA NA NA ...
$ group : chr "Plants" "Plants" "Plants" "Plants" ...
$ abundance : num 2 6 2 7 5 1 22 12 3 5 ...
$ abundanceUnit : chr "count" "count" "count" "count" ...
$ refID : chr "2" "2" "2" "2" ...
- attr(*, "chronosphere")=List of 13
..$ dat : chr "biodeeptime"
..$ var : chr "denormalized"
..$ res : logi NA
..$ ver : num 1
..$ datafile : chr "biodeeptime.rds"
..$ item : int 702
..$ reference : chr "Jansen A. Smith, Marina C. Rillo, Ádám T. Kocsis, Maria Dornelas, David Fastovich, Huai-Hsuan M. Huang, Lukas J"| __truncated__
..$ bibtex : chr "@misc{jansen_a_smith_2023_8154672,\n author = {Jansen A. Smith and\nMarina C. Rillo and\nÁdám T. Kocsis and\nMa"| __truncated__
..$ downloadDate: POSIXct[1:1], format: "2023-07-20 09:51:33"
..$ publishDate : chr "2023-07-12"
..$ infoURL : logi NA
..$ API : logi NA
..$ additional : list()
Basic analyses
The number of time series in the database:
length(unique(bdt$seriesID))
[1] 10062
The number of records in the database:
length(bdt$db)
[1] 7437847
The number of unique sampling locations:
nrow(unique(bdt[, c("long", "lat")]))
[1] 8752
The oldest record (relative to 1950) in each database:
bdt %>% group_by(db) %>% summarize(max = max(age))
# A tibble: 9 × 2
db max
<chr> <dbl>
1 BioTIME 49.4
2 Direct uploads 1146200
3 Geobiodiversity Database 451050000.
4 MARBEN 77200000
5 Neotoma 23900000
6 Neptune SandBox 151075752
7 Paleobiology Database 150889174.
8 SedTraps -28.4
9 Triton 65997000
Finding the mean age (relative to 1950) of a sample from modern databases (BioTIME and SedTraps):
modern <- bdt %>%
filter(db == "BioTIME" | db == "SedTraps") ## filtering to only modern data
mean(modern$age)
[1] -44.50505
Finding the mean age (relative to 1950) of a sample from fossil databases:
fossil <- bdt %>%
filter(db != "BioTIME" & db != "SedTraps") ## filtering to exclude modern data
mean(fossil$age)
[1] 5087525
For additional analyses and visualization, data summarization and manipulation can be done as follows:
## this manipulation summarizes information for each unique time series
overview <- bdt %>%
group_by(seriesID) %>%
dplyr::summarise(db = unique(db), ## source database
#environment = unique(environment), ## broadly defined environment
group = unique(group), ## taxonomic group
lat = unique(lat), ## latitude
long = unique(long), ## longitude
#abundType = unique(abundanceUnit), ## abundance type of records
samples = length(unique(sampleID)), ## number of samples
richness = length(unique(analyzedTaxon)), ## number of unique species
meanAge = mean(age, na.rm = TRUE), ## mean age of samples
minAge = min(age, na.rm = TRUE), ## minimum age of a sample
maxAge = max(age, na.rm = TRUE), ## maximum age of a sample
extent = maxAge - minAge) ## temporal extent (duration) of the time series
Warning: Returning more (or less) than 1 row per `summarise()` group was deprecated in
dplyr 1.1.0.
ℹ Please use `reframe()` instead.
ℹ When switching from `summarise()` to `reframe()`, remember that `reframe()`
always returns an ungrouped data frame and adjust accordingly.
`summarise()` has grouped output by 'seriesID'. You can override using the
`.groups` argument.
Visualizing the data
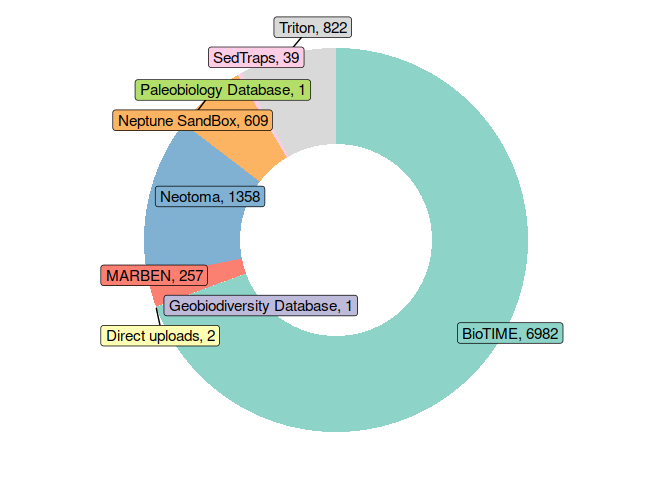
Create a donut plot showing the contribution of source databases to BioDeepTime:
## donut plot for proportion contribution of each database
databases <- overview %>%
group_by(db) %>%
dplyr::summarise(count = n())
# Compute percentages
databases$fraction <- databases$count / sum(databases$count)
# Compute the cumulative percentages (top of each rectangle)
databases$ymax <- cumsum(databases$fraction)
# Compute the bottom of each rectangle
databases$ymin <- c(0, head(databases$ymax, n=-1))
# Compute label position
databases$labelPosition <- (databases$ymax + databases$ymin)/2
# Compute a good label
databases$label <- paste0(databases$db, ", ", databases$count)
# # Make the plot
ggplot(databases, aes(ymax=ymax, ymin=ymin, xmax=4, xmin=3, fill=db)) +
geom_rect() +
geom_label_repel(x = 4, aes(y=labelPosition, label=label), size=4) + ## x controls label position (inside/outside donut)
scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Set3") +
coord_polar(theta="y") +
xlim(c(2, 4)) +
theme_void() +
theme(legend.position = "none") ## controls the presence of a legend